Cybersecurity is now essential for society’s stability and safety. As the digital world changes, cyber threats become more complex and can cause greater harm. In response to this pressing challenge, the European Union has updated its legislative framework to strengthen the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure and services across Europe.
The Network and Information Security 2 (NIS2) (Directive (EU) 2022/2555) is a robust evolution of the EU’s commitment to securing its digital infrastructure. This latest directive expands upon the foundations laid by its predecessor (NIS Directive (EU) 2016/1148, which is repealed by NIS2 after 18 October 2024), aiming to unify and escalate cybersecurity measures across member states.
NIS2 is not just a formality—it’s a significant overhaul with wide-reaching implications. In this post, we’ll delve into what NIS2 is, its scope, requirements, and impacts, and how entities can prepare for compliance. Stay informed as we explore this pivotal regulation poised to redefine Europe’s cybersecurity landscape.
What is NIS2?

NIS2 is the European Union’s upgraded directive focused on improving cybersecurity across all member states by setting higher security standards for critical and important entities (including essential services as defined by Directives such as EU 2022/2557 and Commission Requirements for medium-sized enterprises in 2003/361/EC).
NIS2 extends the vision of its predecessor by focusing on national capabilities, enhancing collaboration across the bloc, and bringing a broader range of sectors under its ambit. This includes energy, transport, banking, and health, among others. By doing so, it acknowledges that the security of network and information systems is vital for ensuring the continuity of these essential services that underpin the society and economy of the EU.
The directive directly responds to the lessons learned from past cybersecurity incidents. It aims to eliminate inconsistencies in cybersecurity preparedness across member states and promote a high common level of cybersecurity across the Union.
The Scope of NIS2
NIS2 significantly broadens the sectors and entities required to meet enhanced cybersecurity standards, including digital service providers and critical public services.
Articles 2 and 3 outline the directive’s scope and the entities it covers. In summary, the directive applies to entities in sectors listed in Annex I or II (e.g., Energy, Transport, Health, etc.) that qualify as medium-sized enterprises. However, it also extends the applicability criteria to additional entities (e.g. DNS service providers), regardless of whether they meet the medium-size criteria.
This directive brings about a wave of changes by encompassing more sectors than previously covered by the original NIS Directive (2016/1148). For instance, entities within sectors such as energy, transport, health, and digital infrastructure now find themselves within the directive’s widened scope. Furthermore, NIS2 acknowledges the shifting dynamics of cybersecurity by including medium and large companies in important economic sectors like postal, wastewater, public administration, and space.
The expanded scope of NIS2 ensures that a more uniform set of cybersecurity practices is applied throughout the internal market. This strategic move is to manage risks and resist cross-border cyber threats effectively, promoting a level playing field and uniform preparedness among member states.
Key Requirements of NIS2
NIS2 mandates entities to implement strong cybersecurity measures, including risk management processes and incident reporting protocols.
It’s important to note that NIS2 is a directive, meaning that EU countries must incorporate it into their national laws. Consequently, the language of the NIS2 directive mandates that ‘Member States’ undertake specific actions to ensure compliance by critical and important entities with the outlined requirements. However, articles 20 to 25 in Chapter IV, ‘Cybersecurity Risk Management Measures and Reporting Obligations,’ clearly demonstrate what the legislator expects important and critical entities to undertake.
Article 21, ‘Cybersecurity risk-management measures,’ outlines perhaps the most crucial obligation of the entities, which is implementing appropriate and proportionate measures to manage cybersecurity risks. This wording is similar to comparable frameworks where security controls must be ‘appropriate’ or ‘adequate,’ such as SB327, which mandates manufacturers to include a reasonable security feature’ in devices. Similarly, the EU AI Act, Article 15, requires ensuring that the cybersecurity measures for high-risk AI systems are proportionate to the relevant risks, and the EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA: 3.1.1) mandates maintaining an appropriate level of cybersecurity based on the identified risks.
The following bullet point list summarizes the responsibility presented in articles 20 to 25:
- Management bodies of essential and important entities:
- Approve cybersecurity risk-management measures.
- Oversee the implementation of cybersecurity risk-management measures.
- Members of management bodies of essential and important entities
- Participate in cybersecurity training.
- Encourage regular cybersecurity training for employees within their organizations.
- Essential and important entities implement appropriate and proportionate technical, operational, and organizational measures to manage cybersecurity risks.
- Reporting requirements for essential and important entities:
- Notify authorities promptly of any significant incidents impacting service provision.
- Communicate promptly with affected service recipients regarding significant cyber threats.
- Standardization: Adoption of European and international standards is encouraged.
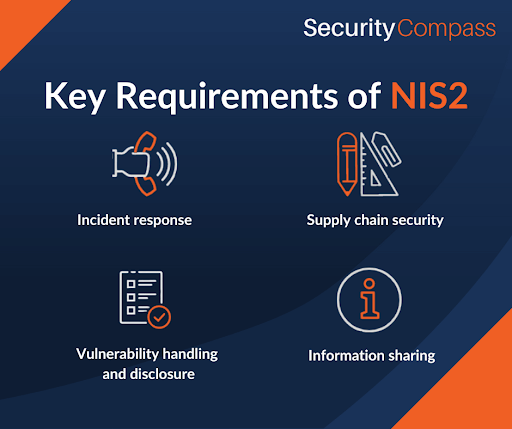
Within Article 21 and when it comes to implementing appropriate measures, key requirements include:
- Incident response
- Business continuity
- Supply chain security
- Vulnerability handling and disclosure
- Human resource security, access control, and asset management
- Cryptography, Multi-Factor Authentication, and other security measures
Additionally, NIS2 strengthens the incident reporting requirements. It introduces more stringent supervisory measures for national authorities and prioritizes stringent enforcement requirements. Companies must notify relevant national authorities of any significant cyber incidents without undue delay—in some cases, within 24 hours of becoming aware of the incident.
Entities falling under the directive must be prepared for stricter oversight and enforcement. Compliance with NIS2 will not be optional, and adherence to its requirements will become a cornerstone of enterprise risk management strategies across the EU.
The Impact of NIS2 on Businesses
Businesses within the NIS2 scope will need to enhance their cybersecurity strategies, which could potentially affect operations, compliance efforts, and investment priorities.
The introduction of NIS2 will require affected organizations to carefully evaluate and upgrade their current cybersecurity and data protection regimes. This elevation in security standards will likely influence several aspects of business operations.
This new directive could translate into increased investments in cybersecurity infrastructure, training, and personnel for many organizations. It will be crucial to manage these investments effectively while avoiding disruptions to daily operations.
Additionally, businesses may face a learning curve when embedding the directive’s requirements into their corporate culture, which will likely necessitate a substantial commitment to cybersecurity awareness and training.
Compliance will not just be a matter of avoiding penalties; it will also be about securing customer trust and ensuring the smooth operation of cross-border services within the EU’s Digital Single Market. Organizations should view compliance as an opportunity to reinforce their commitment to cybersecurity, potentially becoming a competitive advantage.
The integration of NIS2’s requirements into existing compliance frameworks can present challenges, but it also offers a clear blueprint that helps demystify what concrete cybersecurity measures companies need to take.
For many, this may mean revisiting risk assessment and management strategies, updating incident response plans, and fostering stronger partnerships with public authorities and industry groups.
By preparing now, businesses can transform the necessity of NIS2 compliance into an asset for organizational resilience and longevity in the increasingly cybersecurity-focused business environment.
NIS2 vs. Other Cybersecurity Regulations
Organizations operating in Europe are increasingly seeking to harmonize their compliance efforts across various mandates, aiming for a cohesive strategy that satisfies all legal and regulatory obligations and fosters strong cybersecurity practices.
There are several EU regulations and frameworks similar to NIS2 which are worth mentioning. For instance, the Radio Equipment Directive 2014/53/EU (RED) regulates radio equipment placed on the EU market. The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) focuses on operational resilience within the financial sector. The EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) aims to improve cybersecurity by establishing common standards for products with digital elements. Lastly, the EU AI Act promotes trustworthy AI.
Although these regulations and frameworks may share some common aspects, each has its distinct target and focus.
Preparing for NIS2 Compliance

Organizations should take proactive steps to align with NIS2 requirements, from assessing current cybersecurity postures to developing comprehensive incident response plans.
As the NIS2 Directive looms on the horizon, businesses falling within its ambit must start preparing to ensure they meet its stringent requirements.
Here are some foundational steps that organizations should consider to align with NIS2:
| Conduct a Gap Analysis: | Assess current cybersecurity measures against NIS2 requirements to identify areas for improvement. |
| Develop a Robust Risk Management Framework: | Establish and maintain a risk management process that includes regular security audits, assessments, and testing. |
| Enhance Incident Response Capabilities: | Prepare action plans and recovery procedures to effectively manage cyber incidents within the reporting timeframes mandated by NIS2. |
| Foster a Culture of Cybersecurity: | Invest in security awareness training to ensure that staff at all levels understand their roles in maintaining cybersecurity. |
| Review Supply Chain Risks: | Strengthen oversight and control over third-party providers to mitigate supply chain vulnerabilities. |
| Establish Clear Communication Channels: | Set up protocols for information sharing with national authorities and industry partners regarding cyber threats and incidents. |
For each of these steps, businesses may find it helpful to leverage compliance tools and seek out professional advice to navigate the complexities of meeting NIS2 requirements.
It’s worth emphasizing the importance of not waiting until the last moment to prepare for NIS2. The sooner an organization starts its journey toward alignment, the more seamless its path to compliance will be.
Furthermore, given the dynamic nature of cybersecurity threats, continual review and adaptation of security practices will be crucial for maintaining compliance and safeguarding business operations over time.
Compliance is not a one-off event but an ongoing commitment to operational excellence and resilience in the face of cyber threats.
Challenges and Considerations
Entities face challenges in achieving NIS2 compliance, from technical complexity to aligning multi-national processes with the directive’s requirements.
Compliance with NIS2 can be a daunting prospect, particularly for businesses that operate across multiple jurisdictions or have not previously been subject to cybersecurity regulations as strict as those proposed in NIS2.
Some of the common challenges include:
- Technical Complexity: Implementing the necessary technical measures to address the full spectrum of cyber risks can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Resource Allocation: Organizations may need help with allocating adequate budget and staffing towards compliance efforts, particularly in industries with thin margins or other competing priorities.
- Legal and Regulatory Hurdles: Understanding and interpreting the legislative nuances of NIS2 and how it interacts with other regulations can be challenging.
- International Operations: Multinational entities need to consider reconciling NIS2 requirements with those that might apply in other countries they operate in, which could have contrasting cybersecurity laws.
Organizations must not only consider these challenges but also look at the broader strategic implications of NIS2:
- Protecting Brand Reputation: Non-compliance or breaches due to inadequate cybersecurity could lead to loss of customer trust and potentially severe reputational damage.
- Enforcement and Penalties: NIS2 proposes harsh penalties for non-compliance, including fines, which could significantly impact organizations.
- Privacy Concerns: Adapting incident response plans to align with NIS2 should be done with privacy considerations in mind, ensuring personal data is handled in compliance with GDPR and other applicable privacy laws.
It’s essential to examine these challenges through a strategic lens, viewing compliance not as a burden but as a fundamental aspect of business continuity and corporate reputation. It calls for a cross-functional approach where legal, IT, cybersecurity, and compliance teams work collaboratively to achieve a common goal.
By considering these challenges carefully and planning accordingly, organizations can work toward turning potential hurdles into opportunities for improving their cybersecurity readiness.
The Role of Security Compass in NIS2 Compliance
Security Compass offers tools and insights that can assist organizations in meeting the requirements of NIS2 efficiently and effectively.
While this post aims to be educational rather than promotional, it’s pertinent to mention how companies like Security Compass could support businesses on their journey toward NIS2 compliance. Security Compass provides a suite of services that empower organizations to embed security into their processes proactively from the outset.
Here’s how Security Compass can facilitate compliance with NIS2:
| Security by Design: | With Security Compass’s proactive approach, organizations can integrate security early in the development lifecycle, addressing potential vulnerabilities before they become threats. |
| Streamlined Compliance: | Security Compass’s tools can help streamline the path toward compliance with NIS2, making it easier to manage the directive’s complex requirements. |
| Developer-Centric Solutions: | By focusing on solutions that fit seamlessly into developers’ workflows, Security Compass helps ensure that security measures do not impede development teams’ agility and efficiency. |
| Training and Awareness: | Security Compass provides tailored training solutions designed to raise security awareness and competencies across all levels of an organization. |
The benefits of aligning with a partner like Security Compass include easing the burden of compliance and ensuring that the organization’s security practices are sustainable and scalable. This allows businesses to focus on critical operations while navigating the evolving cybersecurity landscape.
While Security Compass aims to be a valuable ally in the compliance efforts, its role is to support and enhance the organization’s capabilities, fostering a collaborative approach to cybersecurity that reflects the shared responsibility outlined in NIS2.
Conclusion
Embracing NIS2 compliance is crucial for the security and resilience of critical sectors in the EU, and timely action is key to meeting the directive’s requirements.
As we wrap up our exploration of the NIS2 Directive, it’s evident that its challenges are matched by its potential benefits. Strengthening our collective cybersecurity is not just about protecting individual organizations—it’s about ensuring the stability and trustworthiness of the entire digital ecosystem.
For companies impacted by NIS2, the path ahead involves a strategic blend of robust cybersecurity measures, continuous learning, and collaboration with regulatory bodies. Moreover, successfully navigating the compliance journey can offer more than just avoidance of penalties—it can lead to competitive advantage, improved customer trust, and even business growth.
Leaders across all relevant sectors should consider NIS2 compliance integral to their operational roadmap. By taking proactive steps today, organizations will not only align with regulatory requirements but also contribute to a more secure, resilient digital future for all.
In conclusion, NIS2 underscores the importance of a harmonized and fortified cybersecurity landscape. Businesses that recognize and act upon the importance of these directives will not only comply with the law but will also play an essential part in safeguarding society’s digital infrastructure.
Now is the time for action, reflection, and embracing the opportunities presented by enhanced cybersecurity standards.
Contact us today to learn more.